Also called an O-ring or washer, a gasket is a handy material for sealing gaps when connecting two parts. But with the various types of gaskets out there, it can be tricky and even overwhelming to choose the right kind of gasket for your project.
Some gaskets are resistant to chemicals and corrosion, while others wear out faster over time. Whether you’re using one to fix your motorcycle or car or do mechanic work, house repairs, or DIY projects, here’s a visual guide to help you decide which gasket is the best option for what you’ll use it for.
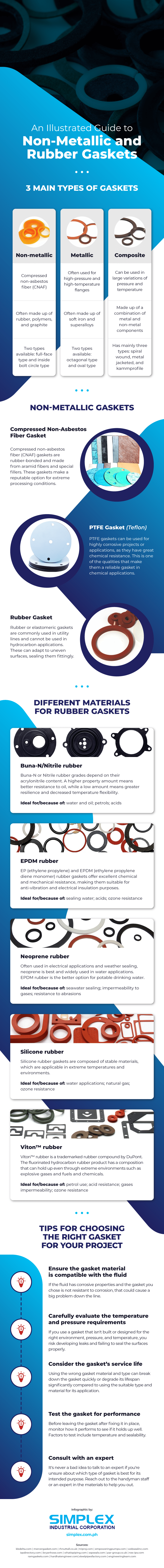
3 Main Types of Gaskets
There are various types of gaskets you can use for different applications, environments, and fluid and temperature conditions. Ensure no leaking happens from the flange joint by choosing the right gasket type and material for your project. Below are the three varieties used that you should know:
1. Non-metallic
Also known as soft gaskets, non-metallic gaskets are the most common type used for easy compression for low-pressure and low-temperature applications, except for graphite gaskets.
They can be made with a compressed non-asbestos fiber (CNAF) gasket, a PTFE gasket (Teflon), graphite, or rubber. Graphite gaskets can be used for temperatures up to 460°C.
Non-metallic gaskets are easily available in hardware stores and are the most affordable among the types.
2. Metallic
Metallic gaskets or ring gaskets are made from soft iron, stainless steel, low carbon steel, monel, and inconel. Because of their robust material, they can be utilized in high temperature and pressure flanges. These types can withstand temperatures as high as 1200°C.
There are two types of metallic gasket: octagonal and oval. Considering its solid material and characteristics, metallic gaskets cost more than non-metallic ones. Sealing metallic gaskets securely and effectively also requires high tension bolting.
3. Composite
This type is a combination of metal and non-metal components, which is why it’s also known as a semi-metallic gasket. Depending on the service requirement, you can do various combinations with this type and can be used in an extensive range of environments for different pressure and temperature applications.
There are three common types of composite gaskets, namely kammprofile, metal jacketed, and spiral wound. Because they use a combination of non-metal and metal materials, they are usually more affordable.
Non-Metallic Gaskets
Since non-metallic gaskets are the most common and easily available type in the market, learn more about their subtypes and applications below.
-
Compressed Non-Asbestos Fiber Gasket
Compressed non-asbestos fiber (CNAF) gaskets are made with high-temperature and pressure aramid fibers and special fillers that make an excellent choice for sealing, thermal, and mechanical use. These non-asbestos counterparts offer similar strength and resistance abilities without the toxicity of asbestos fibers.
CNAF gaskets can be used in various applications and environments such as around chemicals, gases, water, steam, and acids.
-
PTFE Gasket (Teflon)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets provide great bonding application, which means they’re impervious to chemical reactions and corrosion. It also offers insulating capabilities, excellent toughness, and impact strength. Typically, PTFE gaskets are approved as a food-grade material, making them applicable to medical and food production industries.
However, a few chemicals, including magnesium and fluorinating agents, can still affect their lifespan and degrade their quality. In addition, they don’t perform as well as non-asbestos gasket materials when it comes to temperature, pressure, and mechanical use.
-
Rubber Gasket
Rubber gaskets are known for their excellent compression characteristics using polymer materials that provide high elasticity. Rubber gaskets are best used in utility lines since they can adapt to irregular surfaces properly, providing a tight seal.
In most cases, synthetic rubber can bear up against aggressive weather conditions. However, they cannot be used for pipelines in hydrocarbon services and applications with temperatures above 120°C—inferior to PTFE gaskets.
Different Materials for Rubber Gaskets
-
Buna-N/Nitrile rubber
Also known as Butadiene Acrylonitrile or NBR rubber, Buna-N rubber gaskets have grades that vary based on their acrylonitrile properties. A higher acrylonitrile content means excellent oil resistance, while a lower content can offer greater resilience and low-temperature elasticity.
Buna-N rubber provides good resistance to solvents, lubricants, oils, and petrols. However, they don’t stand well against ozone resistance. As such, they are a better match for oils, fuels, fats, and other liquids that contain these.
-
EPDM rubber
Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber works well with various materials and shows great resistance to aggressive weather conditions. This type of rubber can withstand the destructive effects of heat, ozone exposure, oxygen, weather, steam, and other chemicals, acids, and oils.
-
Neoprene rubber
Also known as polychloroprene or chloroprene rubber, neoprene rubber gaskets are made from robust, synthetic materials and are typically used in weather sealing and electrical applications. Neoprene rubber gaskets can be suitable for use in oils, fats, and salt or freshwater applications (but not drinking water). However, they are not recommended for projects involving ketones and aromatic hydrocarbons.
-
Silicone rubber
Silicone rubber offers exceptional elasticity properties, making it a versatile and stable material used in low and high temperatures. This type provides good resistance to UV light, aging, oxygen, ozone resistance, aggressive weather conditions, and extreme temperatures. Gaskets made from silicone can be used in food production and pharmaceutical applications.
-
Viton™ rubber
Viton™ rubber is a fluoropolymer elastomer-based synthetic rubber that is under the brand name DuPont. This material can stand against extreme environments and temperatures. Because of its robust characteristics, it can be used in fuels, explosive gases, and hazardous chemicals such as those used in the oil and mining industries.
Tips for Choosing the Right Gasket for Your Project
Gaskets can be used for different purposes, including noise reduction, tight sealing, and anti-vibration. Here are tips to help you know which type and material to get to ensure it delivers according to your project’s needs.
-
Ensure the gasket material is compatible with the fluid
Choose a gasket that is designed to withstand a specific fluid’s movement. Gaskets eliminate gaps to ensure the fluid moves through, but if their material isn’t designed for the chemical makeup of the fluid it will handle, leakage and other serious problems may occur.
-
Carefully evaluate the temperature and pressure requirements
The myriad of gasket types and materials allow you to find a suitable one depending on factors like the temperature and pressure where it will be used. For example, metallic gaskets can match the high pressures in gas and oil. Meanwhile, non-metallic gaskets aren’t the best option for fluid resistance that is too pressurized.
-
Consider the gasket’s service life
Opting for a gasket that isn’t the suitable material, design, or type for the application may reduce its lifespan significantly. The right type of gasket can last for its intended service life, but the wrong one can deteriorate faster than you expect since it’s not compatible with the usage.
-
Test the gasket for performance
Proper testing of the gasket is a must. You could see if it performs well as it’s supposed to and meets and withstands the requirements for the application. Check how it performs in low or high temperatures, pressure, compression, resistance, chemical degradation, abrasion, and sealability.
-
Consult with an expert
When in doubt, ask for assistance to help you choose the right type of gasket for your project, especially if you’re doing it by yourself and you’re unfamiliar with gaskets. You can always reach out to a gasket design engineer or technical support from gasket distributors like Simplex for expert recommendations whenever you’re uncertain about which material to use.
Final Thoughts
Gaskets play a crucial role in keeping things in place and preventing leakage of air, water, gas, oil, fuel, and other fluids in various applications. That’s why you must understand its different types, materials, and usage to help you make the right choice.
Simplex is a premium distributor of professional-grade gaskets and other high-quality engineering parts in the Philippines. Feel free to browse the shop to find the specific type of gasket or other items you’re looking for to complete your project.